How eGFR and Other Key Kidney Tests Help Detect Kidney Disease Early
04/08/2025
Did you know that chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a growing concern, affecting approximately 37 million adults in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The alarming fact is that 90% of people with CKD don’t know they have it until it progresses to more severe stages.
That’s why kidney function tests, including the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) test and creatinine blood test, are crucial in detecting problems early and managing CKD effectively.
If CKD progresses, treatment options like dialysis or a kidney transplant may become necessary. Many patients now prefer home dialysis as a more flexible and convenient alternative to in-center treatments, allowing for greater independence and improved quality of life. Learn more about home dialysis here.
What is eGFR and Why Does It Matter?
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is a key indicator of how well your kidneys filter blood. It is calculated based on creatinine levels, age, sex, and race and helps determine the stage of kidney disease.
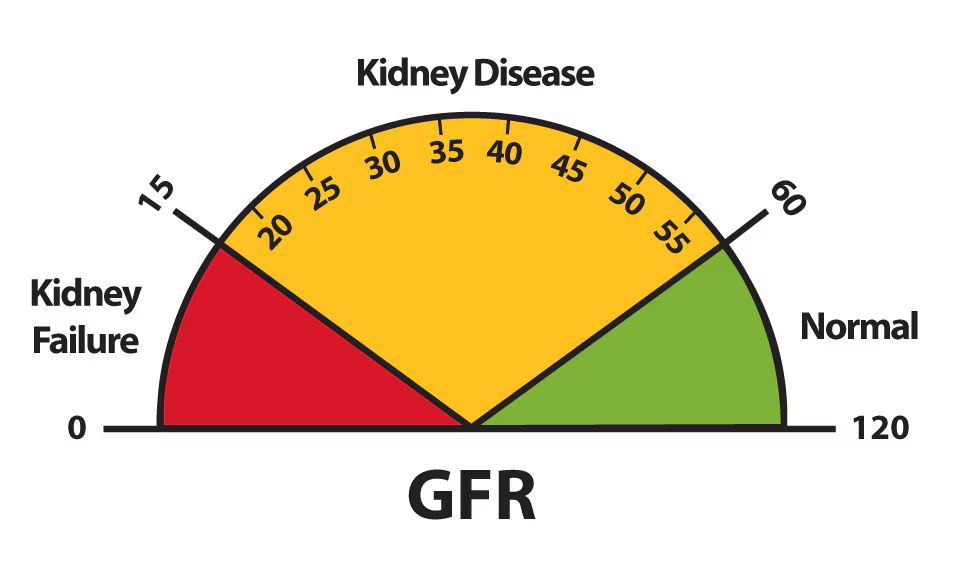
Understanding eGFR Levels
| eGFR Level (mL/min) | Kidney Function |
| 90+ | Normal kidney function |
| 60–89 | Mildly decreased function (Early signs of CKD) |
| 30–59 | Moderate CKD (Stage 3) |
| 15–29 | Severe CKD (Stage 4) |
| Less than 15 | Kidney failure (Dialysis required) |
A low eGFR may indicate kidney damage, requiring additional tests to confirm results.
How eGFR Calculators Help Monitor Kidney Health
Kidney disease often progresses silently, making early detection crucial. One of the best ways to assess kidney function is by using an eGFR calculator, which estimates how well your kidneys are filtering waste from your blood.
What is an eGFR Calculator?
An eGFR (Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate) Calculator is a simple yet effective tool that helps estimate kidney function using key factors like:
- Serum Creatinine Levels – A waste product measured in the blood
- Age – Kidney function naturally declines with age
- Sex – Males and females have different normal kidney function ranges
- Other Factors – Some formulas adjust for body size and race
The eGFR result helps determine chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages and guides doctors in treatment planning.
How eGFR is Calculated
The most commonly used CKD-EPI equation estimates eGFR based on the following formula:
- If serum creatinine (Scr) is low:
eGFR=144×(Scr/0.7)−0.329×(0.993age)
- If serum creatinine (Scr) is high:
eGFR=144×(Scr/0.7)−1.209×(0.993age)
(For males, replace 144 with 141 and adjust exponent values accordingly.)
Understanding eGFR Levels
| eGFR Level (mL/min) | Kidney Function |
| 90+ | Normal kidney function |
| 60–89 | Mildly decreased function (Early signs of CKD) |
| 30–59 | Moderate CKD (Stage 3) |
| 15–29 | Severe CKD (Stage 4) |
| Less than 15 | Kidney failure (Dialysis required) |
A low eGFR may indicate kidney damage, requiring additional tests like creatinine blood tests and urine albumin tests to confirm kidney disease.
Why Use an eGFR Calculator?
- Early detection of kidney disease before symptoms appear
- Monitoring CKD progression over time
- Determining medication dosages for kidney patients
- Assessing overall kidney function to guide treatment
Calculate Your eGFR Now
Take control of your kidney health today. Use This eGFR Calculator to quickly estimate your kidney function and understand your results.
Essential Kidney Function Tests You Should Know
1. Creatinine Blood Test
A creatinine blood test measures the amount of creatinine in your blood, a waste product from the normal breakdown of muscle tissue. High creatinine levels may mean you have kidney disease, as your kidneys may not be working properly.
Normal creatinine levels:
- Men: 0.6–1.2 mg/dL
- Women: 0.5–1.1 mg/dL
Since creatinine is a waste product, the body normally filters it out through urine. If levels are high, it may indicate kidney filtration problems.
2. Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test
This blood test measures the amount of waste product in your blood called urea nitrogen. High BUN levels may suggest kidney disease, dehydration, or high protein intake.
3. Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR) Test
The UACR test checks for albumin in your urine, which may be an early sign of kidney disease.
- Normal albumin level: Less than 30 mg/g
- Elevated albumin level: 30 mg/g or higher → Possible kidney damage
A urine test is often used alongside an eGFR test to confirm the cause of your kidney disease.
4. Creatinine Clearance Test
This test measures how effectively your kidneys remove creatinine from your blood over a 24-hour period. It provides further insights into glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and kidney function.
5. Kidney Biopsy
If other test results suggest kidney disease, a kidney biopsy may be necessary. This involves taking a small sample of kidney tissue to identify the cause of your kidney disease.
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and What They Mean
CKD is categorized into five stages based on eGFR levels:
| Stage | eGFR Level | What Happens? |
| Stage 1 | 90+ | Kidney damage, but normal function |
| Stage 2 | 60-89 | Mild decline in kidney function |
| Stage 3 | 30-59 | Moderate CKD; possible symptoms |
| Stage 4 | 15-29 | Severe CKD; preparing for dialysis or a kidney transplant |
| Stage 5 | <15 | Kidney failure; treatment required |
Knowing your kidney numbers (eGFR and creatinine levels) helps monitor CKD progression.
Who is at Risk for Kidney Disease?
Kidney disease often develops slowly and silently, with symptoms appearing in later stages. Identifying risk factors early can help prevent or delay kidney damage. Several conditions and lifestyle choices increase the likelihood of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD) or kidney failure.
1. Diabetes & High Blood Pressure (Leading Causes of CKD)
- Diabetes: High blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste properly.
- Statistic: Up to 40% of people with diabetes develop CKD over time.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Increased pressure in blood vessels can cause kidney scarring and reduced kidney filtration.
- Fact: Uncontrolled high blood pressure is responsible for about 25% of kidney failure cases (National Kidney Foundation).
2. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
- The heart and kidneys work closely together—when heart health declines, kidney function often worsens too.
- Poor blood circulation and narrowed arteries (due to cholesterol buildup) reduce oxygen and nutrient flow to the kidneys, causing damage.
- Study Insight: People with CVD are at higher risk of developing CKD, and vice versa (American Heart Association).
3. Kidney Stones & Frequent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Kidney stones can block urine flow, leading to kidney infections and scarring over time.
- Chronic UTIs can result in inflammation and long-term kidney damage if untreated.
4. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- AKI is a sudden loss of kidney function, often caused by severe dehydration, infections, medication toxicity, or surgery complications.
- Fact: AKI increases the risk of CKD, especially if kidney function does not fully recover (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases).
5. Obesity & Smoking
- Obesity increases inflammation and blood pressure, making the kidneys work harder.
- Smoking damages blood vessels, leading to low eGFR and CKD progression.
- Study Insight: Obese individuals have a higher risk of CKD and faster decline in kidney function (National Institutes of Health(NIH)).
6. Family History of CKD or Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
- Genetics play a role: if a close family member has CKD or PKD, your risk is higher.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder where fluid-filled cysts develop in the kidneys, affecting function over time.
When to See a Nephrologist (Kidney Doctor)?
Warning Signs of Kidney Disease:
- Swelling in legs, feet, or hands (fluid retention)
- Persistent high blood pressure
- Blood in urine (red blood cells may indicate kidney damage)
- Unexplained fatigue, nausea, or appetite loss
- Changes in urination (foamy urine, frequent nighttime urination, or dark-colored urine)
If your eGFR is less than 60 or your creatinine blood test shows abnormal results, consult a kidney specialist immediately.
Treatment Options for Kidney Failure
1. Hemodialysis – The Preferred Choice for Most Patients
When kidney function declines to the point of failure, hemodialysis is the most effective and widely recommended treatment. This process removes waste, excess fluids, and toxins from the blood, performing the vital filtration work that failing kidneys can no longer manage.
- In-Center Hemodialysis: Patients visit a dialysis center multiple times a week for treatment under medical supervision.
- Home Hemodialysis: A more flexible option that allows patients to undergo dialysis at home, offering greater independence and better quality of life.
Many patients are now choosing home hemodialysis for its added convenience and effectiveness.
Worried about the cost of dialysis? Many insurance plans cover dialysis treatments. Learn more about dialysis insurance coverage here.
2. Peritoneal Dialysis – An Alternative, But Not for Everyone
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is another option where a special fluid is introduced into the abdomen to remove toxins and excess fluids. While PD offers more flexibility and does not require a machine during the treatment, it may not be suitable for everyone due to:
- Higher risk of infections (such as peritonitis)
- Less effective toxin removal compared to hemodialysis
- Not recommended for patients with abdominal surgeries or complications
For most individuals with chronic kidney disease, hemodialysis remains the safer, more effective, and more widely supported treatment option. Consulting with a nephrologist can help determine the best approach for managing kidney failure effectively.
Take Charge of Your Kidney Health
Kidney disease can progress silently, but early detection is key. If you’re at risk due to diabetes, high blood pressure, or family history, regular testing can help catch problems early.
For those with kidney failure, hemodialysis is a reliable and effective treatment that helps maintain quality of life. Many patients are now choosing home dialysis for its added flexibility and comfort.
Worried about the cost of dialysis? Many insurance plans cover dialysis treatments.
Learn more about dialysis insurance coverage here
Taking proactive steps to monitor your health, staying active, and following a kidney-friendly diet can make a big difference.
Driven, adaptable, and passionate about personal and professional growth, I bring a unique blend of creativity, problem-solving, and commitment to everything I do. With a strong background in [insert field or industry], I thrive in fast-paced environments where innovation and collaboration are key. I take pride in building strong relationships, delivering high-quality results, and constantly seeking new ways to learn and improve.
Throughout my journey, I’ve embraced challenges as opportunities for growth and continually pushed myself to exceed expectations. I’m highly organized, detail-oriented, and never shy away from taking initiative. Whether working independently or as part of a team, I believe in maintaining a positive attitude and a strong work ethic.